Electric motors power a vast array of machines and systems — from conveyors and pumps to compressors and HVAC units. While these motors are robust and efficient, they are also vulnerable to overheating when overloaded, stalled, or subjected to prolonged high current. Without proper protection, such conditions can lead to costly equipment damage, downtime, or even safety hazards.
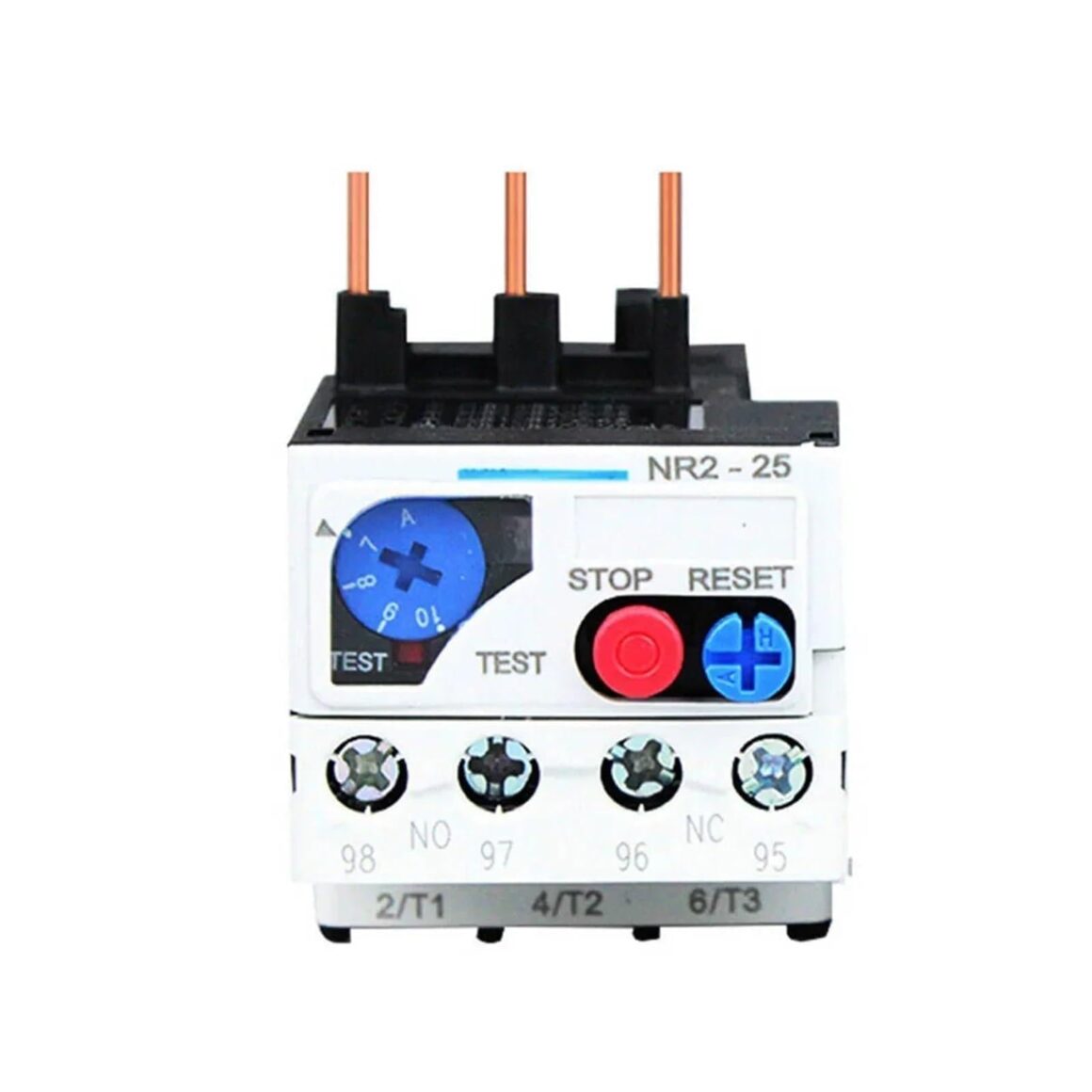
A thermal overload relay is a critical component in motor protection systems. It senses excessive current caused by motor overheating and interrupts power to prevent damage. This mechanical yet precise device plays a significant role in safeguarding electrical systems and ensuring smooth operation in industrial and commercial environments.
What a Thermal Overload Relay Does
At its core, a thermal overload relay monitors the current drawn by an electric motor. When current exceeds safe levels for a sustained period — as during overloads, jammed loads, or frequent starts — the relay’s internal elements heat up. Once these elements reach a certain temperature, the relay trips, disconnecting the motor from its power source.
This mimics the effect of thermal stress within the motor itself. In essence, the relay responds to the motor’s thermal condition rather than just instantaneous current spikes, which may be harmless in short bursts.
Key Components and How It Works
A typical thermal overload relay consists of:
- Bimetallic strips or heaters: These elements heat up based on current flow and bend or expand at predetermined temperatures to trigger a trip.
- Trip mechanism: When the heating element reaches a set point, the trip mechanism actuates and opens the circuit.
- Reset function: After tripping, the relay can be reset either manually or automatically, depending on the design and requirements.
This design provides dependable protection without complex electronics, making thermal overload relays a cost-effective and widely used solution.
Why Motor Protection Is Essential
Motors can experience overload for several reasons — increases in load demand, mechanical friction, poor starting conditions, or electrical imbalances. Without a protective device, these conditions cause excessive heating that can:
- Damage windings inside the motor
- Degrade insulation over time
- Shorten motor lifespan
- Lead to unplanned downtime and maintenance costs
By interrupting power at the right time, thermal overload relays prevent overheating and protect both motors and connected equipment.
Applications Across Industries
Thermal overload relays are used wherever electric motors are employed — in manufacturing plants, water treatment facilities, building automation systems, and HVAC installations, to name a few. Their simplicity and reliability make them suitable for both light-duty and heavy industrial use.
In manufacturing lines, they help avoid disruptions caused by motor failures. In commercial buildings, they protect fans, pumps, and compressors that operate continuously. Across all these applications, the relay’s role remains the same: prevent damage before it escalates.
Setting and Adjustment Considerations
The effectiveness of a thermal overload relay depends on proper settings. The relay is typically adjusted according to the motor’s full-load current rating. This ensures that it trips at a threshold that prevents damage without causing unnecessary interruptions during normal operation.
Factors such as ambient temperature, motor duty cycle, and startup characteristics also influence setting choices. Skilled technicians consider these conditions to fine-tune the relay for optimal protection.
Thermal Overload Relay vs. Other Protection Devices
Thermal overload relays are part of a broader suite of motor protection devices. Unlike instantaneous overcurrent breakers, which respond to sudden spikes, thermal relays are designed to detect sustained excess current that generates heat. This makes them particularly effective for identifying overload conditions rather than short-term surges.
More advanced electronic protection units combine thermal simulation with other protective functions, but the traditional thermal relay remains popular due to its simplicity, affordability, and ease of integration with contactors and starters.
Installation and Integration
These relays are typically paired with motor starters and control circuits. When installed correctly, they provide seamless protection with minimal wiring complexity. Their mechanical design also makes them accessible for routine inspection and maintenance.
Installation should follow manufacturer guidelines and local electrical standards to ensure correct functionality and safety. Regular testing and calibration help verify that the relay responds appropriately under load conditions.

Choosing the Right Relay for Your System
Selecting the appropriate thermal overload relay involves considering:
- The motor’s rated current and application
- Load characteristics and duty cycle
- Environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity
- Whether manual or automatic reset is preferable
Consulting with electrical professionals helps companies choose devices that match both performance needs and safety standards.
Conclusion
A thermal overload relay is a small but vital component in motor protection systems. By sensing sustained overcurrent conditions and interrupting power before damage occurs, it protects motors, enhances operational reliability, and reduces maintenance costs. Its mechanical simplicity, ease of use, and proven effectiveness have made it a cornerstone in electrical control systems across industries.
With proper selection, installation, and adjustment, thermal overload relays continue to safeguard equipment and support efficient, uninterrupted operations — keeping motors running and businesses moving forward.